“How do people become successful?” is a frequently asked question with varied perspectives that change from person to person. Some may say it’s intelligence, some might say it’s talent, a few may say it’s passion and the rest might end up assuming that it’s luck. The concept of success can be influenced by external factors like education and opportunities but the internal factors form its foundational basis. Its shaped by the way an individual thinks, feels, perceives opportunities and challenges and makes the most out of it.
From business tycoons to globally reputed athletes, individuals who achieve greatness often share similar psychological traits that help them grow. Nobody is born successful. It requires cultivating habits, developing a healthy mindset and unlocking their utmost potential. This article will explore the theories of psychology and key aspects that contribute to an individual’s success.
Growth Mindset vs. Fixed Mindset:
Success is not solely understood through an individual’s intelligence, talent, passion or luck. It depends upon the way an individual perceives obstacles and adapts to the challenging environments that help them grow. Carol Dweck proposed the theory of mindset and explained how power of an individual’s beliefs help in understanding the influential framework towards success. An individual with a fixed mindset will believe that distinct factors like intelligence, talent, and, abilities determine how successful an individual will be.
They believe that people are usually born with abilities and potential that is a strong indicator of success rather than opportunities and that will to change. Individuals with a fixed mindset hold a fear of failure and avoid challenges that will expose their weaknesses. They will perceive setbacks or failure as a result of lack of inherent talent or essential resources. It can result in stress, worry, and the fear of failing, which can ultimately hinder growth and learning. People may avoid challenging situations or tasks where they could fail and thus miss learning and growing from them. Such individuals find it hard to achieve success because they assume that “being talented” and “intelligent” will determine their potential rather than hard work.
On the other hand, intelligence and talent can be enhanced through hard work, learning and determination. Individuals with a growth mindset perceive challenges as opportunities, persist through their failures, and work hard to grow. The feelings of disappointment and embarrassment are replaced with consistent efforts and practice. They are intrinsically motivated to cultivate their abilities and learn from their failures to reach their full potential. Rather than sticking to their innate intelligence and talents, they develop through sustained efforts and perseverance.
Dweck’s theory describes that our self-perception of our ability plays a deep role in motivating us and forming a roadway to being successful. The mindset we settle with, decides the way we set goals, cope with failure, and look at setbacks. It is understood that greater success in achieved through unlocking your potential with constant efforts, perseverance and hard work rather than solely determining it on the basis of talent or intelligence.
Read More: Psychology Behind Growth Mindset
Theories related to Growth Mindset:
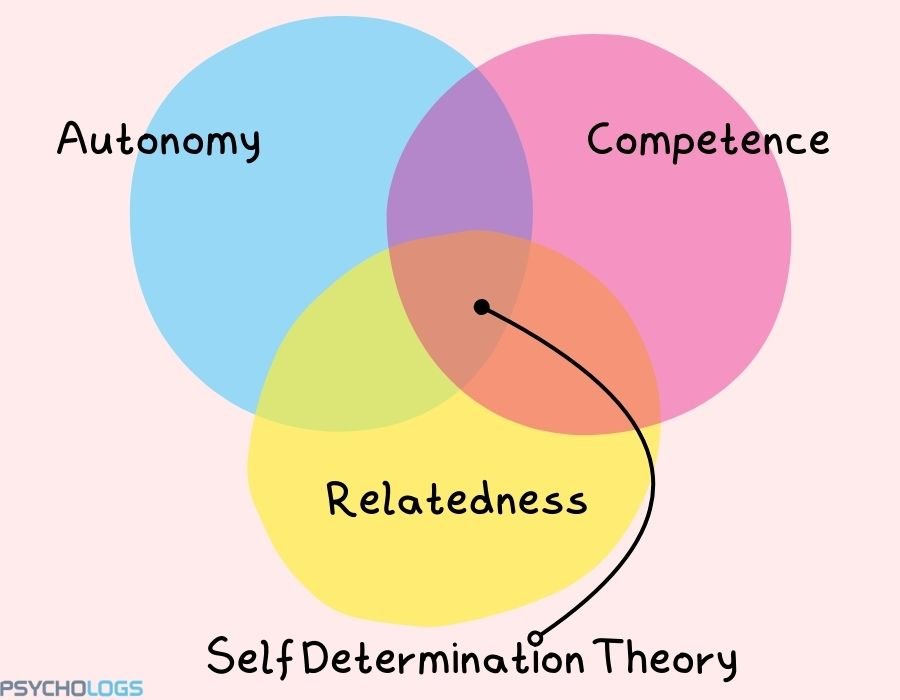
Self determination theory
Self-determination theory proposed by Edward Deci and Richard Ryan emphasizes three psychological needs; autonomy, competence and relatedness that are considered as key determining factors driving human motivation and behaviour towards success. Autonomy refers to an individual’s control over their choices and actions, competence as their interactions with their environment that drive them to engage in those activities and relatedness is the urge to feel connected, understood and accepted by others.
In environments that provide individuals autonomy to make their own choices, challenge them with challenges, and give them useful feedback, there is a stronger likelihood that individuals will remain engaged and successful. For instance, in schools or the workplace, environments that provide autonomy, competence, and relatedness promote enhanced engagement, imagination, and pleasure, all contributing to enhanced success. Also, when individuals feel supported by others, whether personal or workplace. They tend to remain motivated, work well in groups, and weather difficulties.
Thus, Self-Determination Theory helps in understanding that being successful is not only about personal efforts but also about working in a healthy environment where one works and relationships that provide care and motivation. The self-determination theory highlights the importance of intrinsic motivation, supportive environment and fulfillment of psychological needs to pursue challenges, overcome obstacles and achieve success.
Grit and Perseverance
Perseverance and grit have usually been defined as key psychological factors that pay a major part in attaining success, mainly in difficult or long-term situations. Talent, intelligence, and opportunities can preface success but usually are grit—passion and persistence on the path of long-term pursuits—what brings the person his desired results or success. By looking at the interaction of persistence and grit, we become more aware of why some are more likely to succeed than others despite similar adversity. Grit, psychologist Angela Duckworth claims, is a psychological trait comprised of sustained effort and interest for long-term goals.

Unlike other traits such as intelligence or athleticism, grit is not a matter of inherent ability but is all about dogged persistence and effort in the presence of struggle and failure. Duckworth’s own research, particularly in school and workplace contexts, has established that grit predicts success better than other more traditional measures such as IQ or exam scores. In fact, grit has been linked to achievement in sports, business, and education, among other fields, where long-term commitment is required to survive obstacles and to achieve.
Grit is actually a mixture of perseverance and passion. Investigation shows that individuals with high grit levels will succeed in their objectives in very complicated, high-stakes domains as they do not give up when things become difficult. For instance, in education, students who demonstrate grit are most likely to graduate even if they experience academic or personal failures. In sports, tough athletes tend to overcome their physical and psychological barriers to reach their highest possible performance.
Yerkes-Dodson Law
The Yerkes-Dodson Law argues that there is a specific amount of arousal for performance that impacts one’s capacity to perform optimally. This law is one of the building blocks of psychology that connects arousal, performance, and stress to see how stress and motivation affect productivity, accomplishment, and overall success. Through the balance of arousal and performance, one can maximize their efficiency and effectiveness in personal and work-related situations, which can lead to increased success in what they do.
Among the success, drivers is a person’s capability of balancing this fragile relationship between arousal and performance. Achievement generally calls for individuals to be in a state of optimal arousal, which in itself propels motivation, concentration, and productivity. When there is an increased level of stress, individuals may get distressed, and that is deleterious for their performance. Distress destroys cognitive skills with feelings of overwhelm, anxiety, and lack of concentration.
Stress response, when chronic or excess, can contribute to adverse physical and mental states, including burnout, fatigue, and depression. Yerkes-Dodson Law comes into play with relevance to success when people need to learn how to cope with stress and sustain some level of arousal that will trigger best performance without sliding into distress.
Read More: What is Yerkes-Dodson Law?
Personality Traits among Successful People:
Personality traits contribute to an individual’s long term goals, help them manage their emotions effectively and help them navigate through challenges to achieve success.
Resilience:
Resilience is defined as an ability to bounce back from setbacks and persist in the face of difficult times. Individuals often face challenges, difficult circumstances and failures in their life which act as a hurdle towards the journey of success. Resilience helps to recover from difficult situations, learn from the mistakes and keep moving ahead on the path of improvement and learning.

Discipline:
It is the ability to stay committed to one’s goals and stay focused in the process of achieving long-term goals. Organising schedules, making consistent efforts and developing a strong self control helps an individual to stay on track. It helps in building effective habits, time management and overcoming procrastination. Discipline is often about doing things to stay focused on the long term objective instead of getting distracted by short-term gratification. Serena Williams’ consistent hard work, training strategies and time management makes her one of the world’s finest tennis players contributing to her success.
Read More: The Psychology of Discipline
Delayed Gratification:
It is the ability to resist the urge for immediate rewards to prioritise long term goals over short term enjoyments. Delayed gratification is maintained through discipline and consistent efforts. Individuals who stay focused and committed to a goal despite the obstacles and temptations are aware that bigger rewards will come their way. Saving money, working overtime and making small sacrifices help in achieving success. The legendary investor, Warren Buffett is known for his decision-making skills in the investment sector. His vision about the future, impulse control and analytical skills required to invest strategically makes him a renowned public figure.
Emotional Intelligence:
Emotional Intelligence involves the ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions and regulate and understand the emotions of others as well. Individuals with high emotional intelligence engage in social interactions effectively, build strong networks and deal with stress with healthier coping mechanisms. Maintaining clear focus on the goals by effectively managing emotions like anxiety, anger or frustration make it easier to communicate and collaborate with others during conflict resolution.
Read More: What is Emotional Intelligence?
It helps in pursuing goals by aligning your views and passion together while understanding that emotional well-being contributes to one’s success. Oprah Winfrey is an excellent example of how high emotional intelligence can help an individual to connect with her guests on the show and maintain authenticity through her emotional experiences. Her empathetic skills, self-awareness and social interactions make her a trusted and successful interviewer.
Self-Efficacy:
Self-efficacy is referred to as a belief in their own abilities to succeed a certain task or accomplish certain goals. Self-efficacy impacts an individual’s motivation, discipline, perseverance and resilience. Individuals’ efforts and ability attribute to their success and failure. Self-efficacy is strengthened through confidence and capabilities of achieving goals. Like, Michael Jordan’s goal setting behaviors, his confidence in high-pressure environments and excellent performance despite a few failures makes him a testament to self-efficacy. His belief in his abilities and intrinsic motivation helps him to push his limits to perform better.
Role of Habits in Psychology behind Success
Success is a byproduct of repeated, minor actions that people perform automatically, such as getting enough sleep, staying focused at work, or working at a craft on a regular basis. The reason that such behaviors become automatic is that it lowers the mental cost of making decisions so that people remain on course even when motivation wanes. Instead of depending on periodic spurts of motivation or willpower, habits establish a consistent mechanism for long-term success.
This behavior automation is necessary for sustained success because it enables people to save mental energy and put effort consistently towards objectives without depending only on willpower. For instance, a successful business tycoon can have the routine of spending the first hour every day on focused work irrespective of the external situation.
Another fundamental aspect of habits in achieving success is eliminating bad habits and replacing them with better ones. Being successful does not only entail building good habits but also identifying and eliminating bad habits. Understanding what cues and rewards lead to unwanted habits can substitute the habit with a healthier one that yields a similar reward. For instance, if someone has a stress-eating habit late at night, they can substitute this habit with a journaling or meditation routine, giving them a healthier way to deal with stress.
The important thing here is to be consistent and persistent so that the new habit is as automatic as the old habit. Replacing bad habits is also a process that requires self-knowledge and self-awareness. Successful people tend to perform regular self-examination, judging what habits are pushing them forward and which ones are pulling them backward. That knowledge helps them make deliberate decisions about what should change for them to improve their habits and thus their opportunity for success.

Psychological Barriers to Success and Overcoming
Success is not necessarily perfect execution but often incremental improvement toward a goal, learning from mistakes, and evolving in the process. The concept of good enough helps individuals overcome perfectionistic inclinations and the need to achieve perfection and move towards a healthier perspective regarding work and achievement.
Focusing on the process rather than the end product and the recognition that mistakes are valuable learning experiences can actually remove the pressure of perfectionism. Receiving feedback from others and working in an environment where teamwork is promoted can provide one with input that can enable him or her to resist the urge to nitpick everything.
Pursuit of Success with Mental and Physical Well-being
In the modern world, where success is viewed as the end goal in everybody’s life individuals often sacrifice their physical and mental health in this process. Individuals often succumb to high expectations, constant social comparison, demands related to productivity and achievement which impacts their physical health, emotional balance and ultimately mental health.
It is essential to keep your physical health and mental well being at equilibrium in the pursuit of success. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, eating a nutrient rich diet and exercising will help in maintaining optimal brain functioning and physical energy. Overlooking your physical health while focusing on your long-term goals can lead to irritability, lack of concentration and fatigue. True success is achieved when there is a balance between self care achievements and personal fulfillment brings an individual closer towards self-actualization.
Conclusion
The pursuit of success is a personal journey where an individual is required to carefully balance between their ambitions and well-being. True success is not just about accomplishments that you achieve in educational settings or the workplace but it is also finding the purpose of your life, managing stress in effective ways and nurturing a physical body and healthy mind. At the end of the day, success is about living a meaningful and harmonious life where personal growth and happiness is the ultimate goal.
References +
- Baumeister, R. F., Campbell, J. D., Krueger, J. I., & Vohs, K. D. (2003). Does high Self-Esteem cause better performance, interpersonal success, happiness, or healthier lifestyles? Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 4(1), 1–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/1529-1006.01431
- Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in human behavior. In Springer eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2271-7 Duckworth, A. L., Peterson, C., Matthews, M. D., & Kelly, D. R. (2007). Grit: Perseverance and passion for long-term goals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92(6), 1087–1101. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.6.1087
- Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: the new psychology of success. Choice Reviews Online, 44(04), 44–2397. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.44-2397
- Hamann, K., Pilotti, M. a. E., & Wilson, B. M. (2021). What lies beneath: the role of Self-Efficacy, causal attribution habits, and gender in accounting for the success of college students. Education Sciences, 11(7), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11070333
- Seibert, S. E., Crant, J. M., & Kraimer, M. L. (1999). Proactive personality and career success. Journal of Applied Psychology, 84(3), 416–427. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.84.3.416













Leave feedback about this